What is the Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity? Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity is a groundbreaking guide that provides comprehensive insight into the science behind earthquakes.
Editor's Notes: "Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity" have published today date. It is an essential read for anyone interested in understanding the causes and effects of earthquakes.
To help target audience make the right decision, we did some analysis, digging information, made Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity we put together this Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity guide about Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity.
Key differences or Key takeways:
| In-depth explanations | Engaging and accessible writing style |
| Up-to-date information | Stunning visuals and illustrations |

Seismic Waves Vector Illustration. Labeled Educational Earthquake - Source www.pinterest.co.uk
Here's what you'll learn in the Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity guide:
FAQ
Explore commonly asked questions about epicenters, the focal points of seismic activity. Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity

Earthquake Diagram Animation - Source animalia-life.club
Question 1: What exactly is an epicenter?
The epicenter represents the point on Earth's surface directly above the hypocenter, the location where an earthquake originates.
Question 2: How do scientists locate an epicenter?
Seismologists utilize a network of seismic stations to record earthquake waves. By analyzing the time difference between wave arrivals at different stations, they can triangulate the epicenter's location.
Question 3: What factors influence the severity of ground shaking at an epicenter?
Numerous factors contribute to ground shaking intensity, including earthquake magnitude, distance from the epicenter, local geology, and soil conditions.
Question 4: Can epicenters shift during an earthquake sequence?
Yes, in certain instances, the epicenter of an earthquake sequence may migrate over time, indicating the propagation of seismic activity along a fault.
Question 5: What methods are employed to mitigate the impact of earthquakes near epicenters?
Communities implement building codes, earthquake-resistant construction techniques, and early warning systems to reduce damage and enhance public safety near epicenters.
Question 6: How does epicenter research contribute to our understanding of earthquakes?
Epicenter studies play a crucial role in understanding earthquake source mechanisms, fault behavior, and seismic hazard assessment, which are essential for developing effective mitigation strategies.
By unraveling the core of seismic activity at epicenters, scientists gain valuable insights into earthquake processes and empower us to prepare for and mitigate their potential impacts.
Continue exploring our comprehensive guide to Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity for further insights.
Tips
The study of seismic activity is a complex and multifaceted field. By understanding the underlying principles and employing effective strategies, researchers can gain valuable insights into the behavior of earthquakes and their impact on the environment.
Tip 1: Utilize advanced technologies: Employ cutting-edge technologies such as seismic imaging and remote sensing to gather detailed data on earthquake sources and wave propagation. These techniques provide valuable information for identifying seismic hazards and assessing their potential risks.
Tip 2: Collaborate with diverse experts: Engage with a multidisciplinary team of geologists, geophysicists, engineers, and seismologists to gain a comprehensive understanding of seismic activity. Each discipline brings unique perspectives and expertise, enhancing the overall research outcomes.
Tip 3: Analyze historical data: Study historical earthquake records and paleoseismic evidence to identify patterns, recurrence intervals, and potential source regions. This information aids in long-term seismic hazard assessment and forecasting.
Tip 4: Conduct field investigations: Perform field surveys to gather data on fault structures, rock properties, and surface deformation. These observations provide essential insights into the mechanics of earthquakes and their geological context.
Tip 5: Employ numerical modeling: Utilize numerical simulations to model earthquake processes and predict ground motion. These models allow researchers to investigate various scenarios and assess the potential impacts of earthquakes on infrastructure and human populations.
Key Takeaways:
- Incorporating advanced technologies enhances data acquisition and analysis.
- Collaboration fosters interdisciplinary insights and comprehensive understanding.
- Historical analysis provides valuable information for seismic hazard assessment.
- Field investigations offer direct observation of earthquake-related phenomena.
- Numerical modeling aids in predicting earthquake behavior and ground motion.
By implementing these tips, researchers can enhance their understanding of seismic activity, mitigate its risks, and contribute to the safety and resilience of communities.
Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity
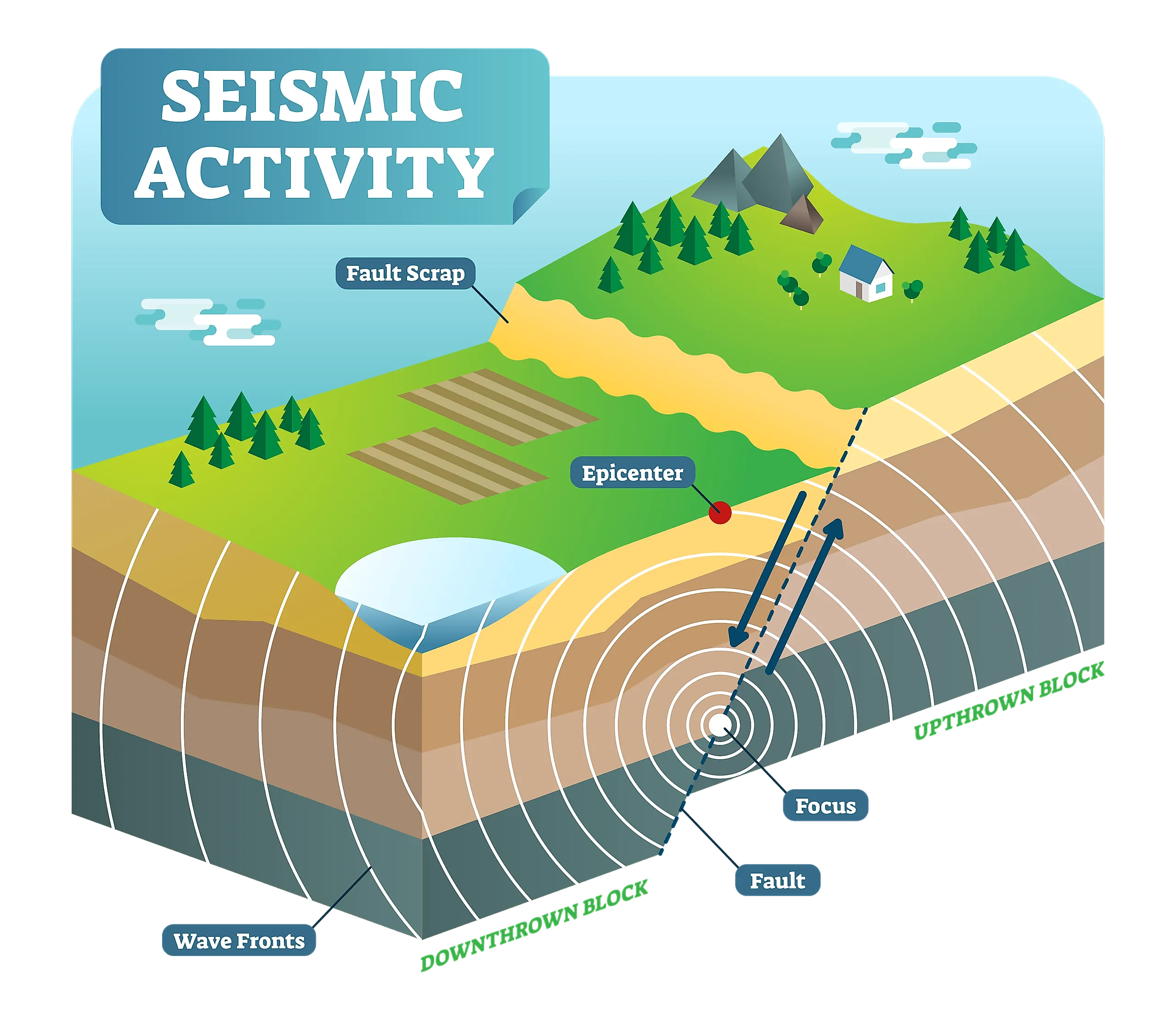
The epicenter, the point on the Earth's surface directly above the hypocenter, the location of the earthquake's initial rupture, is a crucial aspect in understanding seismic activity. Six key aspects delve into its significance:
- Location: Pinpoints the surface projection of the hypocenter.
- Ground Motion: Impacts the severity of shaking experienced at the surface.
- Intensity Mapping: Aids in assessing earthquake damage and risk.
- Early Warning Systems: Provides critical time for preparedness.
- Fault Rupture Analysis: Reveals the extent and characteristics of the earthquake source.
- Tectonic Setting: Highlights the geological context and potential for future activity.

25 Amp Rectifier 5w Tube Amp Guitar Amp Headphones Epicenter with Amp - Source www.walmart.com
Understanding these aspects enhances our ability to mitigate earthquake hazards. For instance, epicenter location guides emergency response efforts. Ground motion data helps design earthquake-resistant structures. Intensity mapping supports land use planning and building codes. Early warning systems provide seconds of advance notice, allowing people to take protective actions. Fault rupture analysis informs seismic hazard assessments, and tectonic setting reveals long-term earthquake patterns. By unraveling the core of seismic activity through these aspects, we gain invaluable insights for safeguarding lives and infrastructure.
Natural Disasters Presentation - Source www.slidemake.com
Epicenter: Unraveling The Core Of Seismic Activity
The epicenter of an earthquake is the point on the Earth's surface directly above the hypocenter, the point where the earthquake rupture begins. The epicenter is important because it is the point at which the earthquake's energy is released and where the ground motion is typically strongest. The epicenter can be located using data from seismographs, which measure the ground motion caused by earthquakes. The epicenter is an important component of the earthquake's magnitude, which is a measure of the earthquake's size.

Dark Photons: The Key to Unraveling the Dark Matter Mystery? - TrendRadars - Source www.trendradars.com
The epicenter of an earthquake is often used to determine the earthquake's magnitude, which is a measure of the earthquake's size. The magnitude of an earthquake is determined by the amount of energy released by the earthquake. The magnitude of an earthquake is measured using the Richter scale, which is a logarithmic scale that ranges from 1 to 10. The Richter scale is based on the amplitude of the seismic waves recorded by seismographs. The amplitude of the seismic waves is a measure of the strength of the ground motion caused by the earthquake.
The epicenter of an earthquake is also used to determine the earthquake's intensity, which is a measure of the earthquake's effects on the ground. The intensity of an earthquake is determined by the amount of damage caused by the earthquake. The intensity of an earthquake is measured using the Modified Mercalli Intensity scale, which is a 12-point scale that ranges from I to XII. The Modified Mercalli Intensity scale is based on the observed effects of the earthquake, such as the amount of damage caused to buildings and the number of people injured or killed.
The epicenter of an earthquake is an important piece of information that can be used to determine the earthquake's magnitude and intensity. The epicenter can also be used to determine the earthquake's location and the areas that are most likely to be affected by the earthquake.