Volcanoes And Earthquakes Information - Source studyngokufikaym.z21.web.core.windows.net
Editor's Note: Understanding Newfoundland's Seismic Activity: A Geological Perspective has published today. This topic is important to read because it can help you understand the seismic activity in Newfoundland and the potential risks associated with it.
We have analyzed and gathered information to assemble this Understanding Newfoundland's Seismic Activity: A Geological Perspective guide to support the target audience to make knowledgeable judgments.
Key differences or Key takeways:
Transition to main article topics
FAQ
This FAQ section provides supplementary information and addresses some common questions about the geological aspects of Newfoundland's seismic activity as discussed in the article Understanding Newfoundland's Seismic Activity: A Geological Perspective.

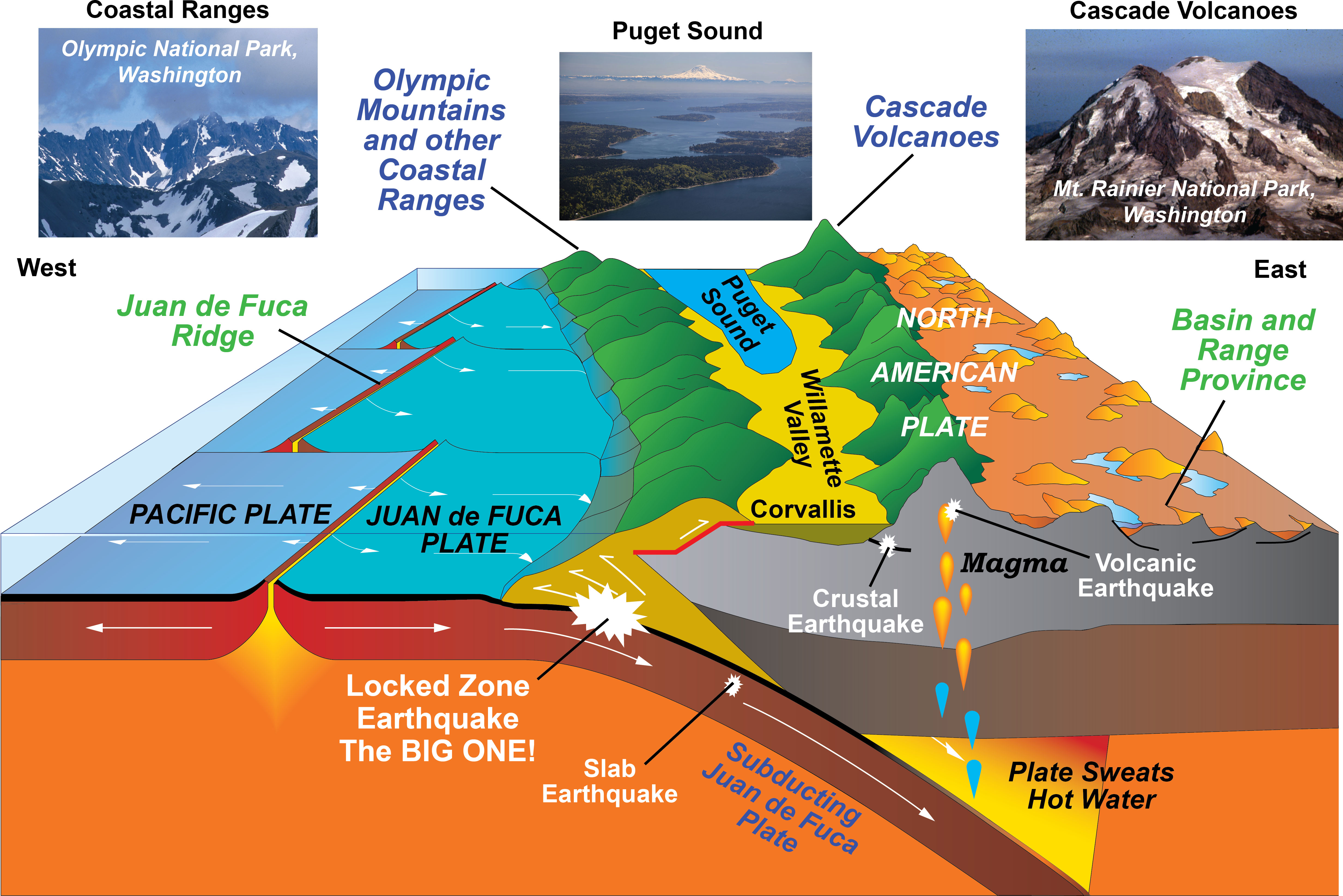
Understanding The Dynamic Earth: A Guide To Today’s Seismic Activity - Source washingtondccitymapminecraft.github.io
Question 1: What is the primary cause of seismic activity in Newfoundland?
The predominant cause of seismic activity in Newfoundland is the movement and interaction between tectonic plates. Newfoundland lies within a zone where two major tectonic plates, the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate, meet. When these plates shift or encounter stress, it can trigger the release of seismic energy, resulting in earthquakes.
Question 2: Are there any known fault lines in Newfoundland?
Yes, there are several known fault lines in Newfoundland. The most prominent ones include the Cabot Fault, the Hermitage Bay Fault, and the Burin Peninsula Fault. These fault lines represent zones of weakness in the Earth's crust where tectonic stress accumulates and can lead to earthquakes.
Question 3: How often do earthquakes occur in Newfoundland?
The frequency of earthquakes in Newfoundland varies. Generally, the region experiences a moderate number of low-magnitude earthquakes, with occasional larger events. The occurrence rate can fluctuate depending on factors such as ongoing tectonic activity and the accumulation and release of seismic energy.
Question 4: What is the largest earthquake ever recorded in Newfoundland?
The largest earthquake recorded in Newfoundland occurred on November 18, 1929, with a magnitude of 7.2. This event caused widespread damage and was felt throughout the province and beyond.
Question 5: How can individuals prepare for the possibility of an earthquake?
Preparing for earthquakes involves taking practical steps to enhance safety and minimize risks. This includes securing heavy furniture, creating an emergency preparedness plan, and storing essential supplies. Familiarity with evacuation routes and having access to communication devices during an event are also important.
Question 6: What should individuals do during an earthquake?
During an earthquake, it is recommended to remain calm and follow safety guidelines. Seek shelter under a sturdy table or in a doorway, away from windows and exterior walls. If outdoors, move to an open area away from buildings and power lines. Once the shaking subsides, check for injuries and report any damage to local authorities.
Understanding the geological factors contributing to Newfoundland's seismic activity is crucial for risk assessment and preparedness. By staying informed and taking necessary precautions, communities can enhance their resilience and mitigate the potential impacts of earthquakes.
For further insights and detailed information, refer to the comprehensive article Understanding Newfoundland's Seismic Activity: A Geological Perspective.
Tips
Understanding the seismic activity of Newfoundland can provide valuable insights into the geological processes occurring in the region and assist in preparing for potential earthquakes.
Tip 1: Monitor Seismic Activity Regularly
By regularly monitoring seismic activity through resources like the Geological Survey of Canada, individuals can stay informed about recent earthquakes and their potential implications. This information can assist in identifying areas at risk and planning appropriate measures.
Tip 2: Understand Earthquake Terminology
Familiarizing oneself with terms such as magnitude, intensity, and epicenter can enhance comprehension of earthquake reports and public advisories. Understanding these concepts allows for more informed decision-making during an earthquake event.
Tip 3: Prepare an Earthquake Plan
Developing a comprehensive earthquake plan, including evacuation routes, emergency supplies, and communication protocols, ensures preparedness in the event of an earthquake. This plan should be practiced regularly to improve its effectiveness.
Tip 4: Secure Heavy Objects
Securing heavy objects like bookcases and appliances can prevent them from toppling over and causing injuries or damage during an earthquake. Proper anchoring techniques can effectively mitigate such risks.
Tip 5: Check Gas and Water Lines
Regularly inspecting gas and water lines for leaks or damage is crucial. In the aftermath of an earthquake, these lines may be compromised, posing fire and flood hazards. If any issues are detected, contact a qualified professional immediately.
Tip 6: Stay Informed About Building Codes
Keeping abreast of the latest building codes and seismic standards ensures that structures are designed and constructed to withstand earthquakes effectively. Adhering to these codes can safeguard buildings and minimize damage.
Tip 7: Know Your Region's Seismic Hazard
Familiarizing oneself with the seismic hazard maps and reports for the region provides insights into the potential intensity and frequency of earthquakes. This knowledge can inform risk assessment and preparedness strategies.
By following these tips, individuals can enhance their understanding of Newfoundland's seismic activity, prepare for potential earthquakes, and work towards mitigating their risks.
To delve deeper into the geological aspects of Newfoundland's seismic activity, refer to the provided article: "Understanding Newfoundland's Seismic Activity: A Geological Perspective."
Understanding Newfoundland's Seismic Activity: A Geological Perspective
Newfoundland's seismic activity is a significant aspect of the region's geological history, influenced by various factors. Understanding this activity requires exploring essential aspects, such as crustal structure, tectonic setting, and historical seismicity, to gain a comprehensive geological perspective.
- Crustal Structure: Newfoundland's crust is relatively thin and seismically active due to its location on the edge of the North American Plate.
- Tectonic Setting: The province lies within the Appalachian Orogen, a collision zone between the North American and African plates.
- Historical Seismicity: Newfoundland has experienced numerous earthquakes throughout its history, with the most significant being the 1929 Grand Banks earthquake.
- Plate Interaction: The interaction between the North American and African plates generates stress and strain, contributing to seismic activity in Newfoundland.
- Fault Systems: The province is home to several fault systems, including the Cabot Fault and the Burin Peninsula Fault.
- Seismic Monitoring: Ongoing seismic monitoring efforts provide valuable data for understanding Newfoundland's seismic activity and assessing potential risks.
These aspects collectively provide a multifaceted understanding of Newfoundland's seismic activity. The thin crust, tectonic setting, and historical seismicity highlight the province's susceptibility to earthquakes. Understanding the plate interaction and fault systems helps identify areas prone to seismic activity. Moreover, seismic monitoring remains crucial for early detection, risk assessment, and preparedness measures against potential seismic events.
Understanding Newfoundland's Seismic Activity: A Geological Perspective
The unique geological setting of Newfoundland makes it a region of particular interest for understanding seismic activity. The island is situated at the convergence of several tectonic plates, including the North American Plate, the Eurasian Plate, and the African Plate. This complex tectonic setting results in a variety of seismic hazards, including earthquakes, tsunamis, and landslides.

Structural Configuration And Tectonics Of The Flemish Cap,, 49% OFF - Source www.micoope.com.gt
In order to mitigate these hazards, it is important to understand the geological processes that give rise to them. This requires a detailed understanding of the region's geology, including the distribution of faults, the thickness and composition of the crust, and the presence of any active volcanoes.
By conducting detailed geological studies, scientists can gain a better understanding of the seismic hazards that Newfoundland faces and develop strategies to mitigate these hazards.
| Geological Process | Seismic Hazard |
|---|---|
| Faulting | Earthquakes |
| Subduction | Tsunamis |
| Volcanism | Landslides |
Conclusion
The study of Newfoundland's seismic activity is a complex and challenging field, but by gaining a better understanding of the geological processes that give rise to seismic hazards, we can develop strategies to mitigate these hazards and reduce their impact on our communities.
Continued research is essential to further our understanding of Newfoundland's seismic activity and to develop effective mitigation strategies.